Prototyping & Additive Manufacturing
Industrial-grade 3D printing services for part prototyping, production runs, and more
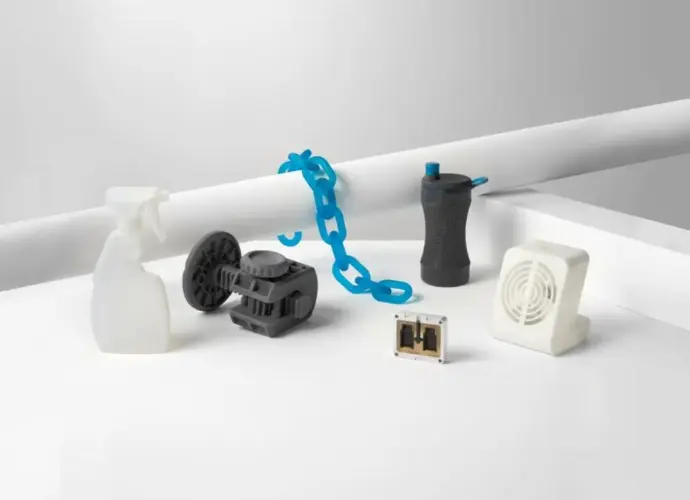
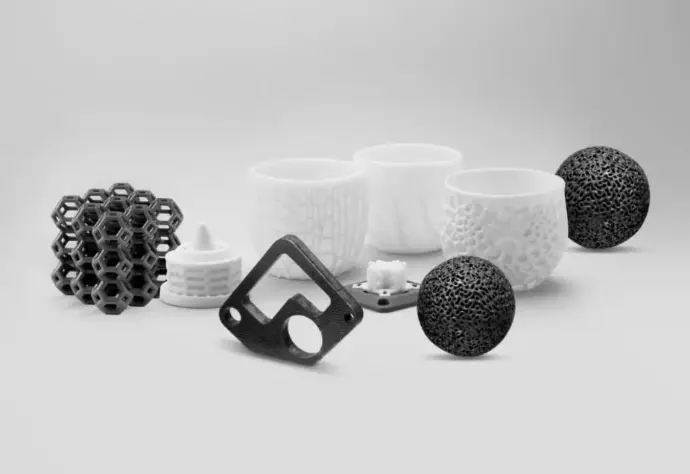



Whether it's a prototype to test the waters or a full production run, our 3D printing lab turns your ideas into real-world parts. We cater to all types of businesses, offering custom 3D-printed solutions for a wide variety of industries and use cases.
With our 3D printing expertise, you can expect customization for your specific application. We work closely with you to print parts that fit your exact needs – whether it’s a unique prototype or functional end-use components. Our lab is equipped for it all.
Choose from a diverse range of resin options for your 3D printing projects. Explore our resin materials to find the perfect match for your parts' requirements.
Resin Material Options
3D printing for a wide variety of applications
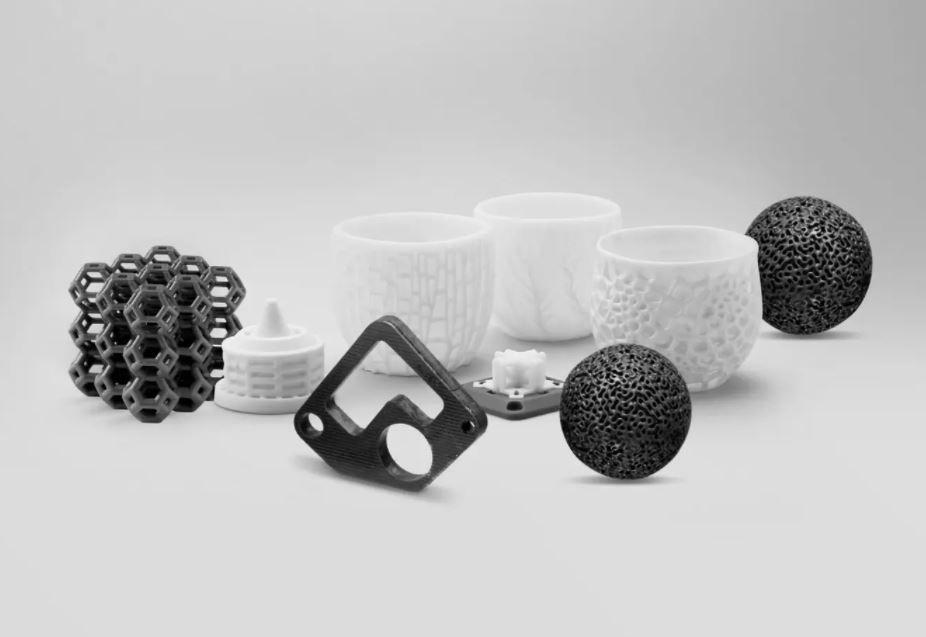
Engineering Resins
Functional prototyping materials.
Our library of versatile, reliable Engineering Resins is formulated to help you reduce costs, iterate faster, and bring better experiences to market. Resin options include:
- Polyurethane Resins: Go beyond the limits of traditional plastic 3D printing and leverage materials that create true, high-performance polyurethane parts.
- Ceramic Resins: For affordable and high-performance technical ceramic 3D printed parts with exceptional thermal, mechanical, and conductive properties.
- Silicone Resins: 100% silicone 3D printing materials to quickly fabricate functional prototypes and short runs in pure silicone.
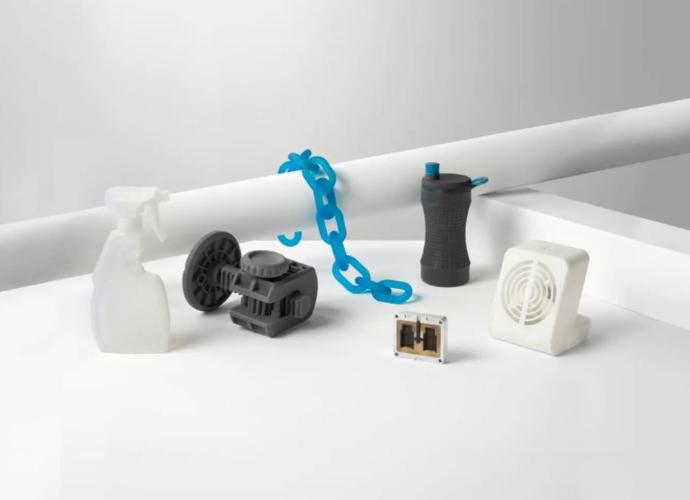

Rigid Resins
Stiff, Strong, Engineering-Grade Prototypes
Choose our family of Rigid Resins when prototyping strong and stiff parts that need to resist bending. Parts made from these materials are thermally and chemically resistant and will be dimensionally stable under load, but will experience brittle failure if pushed to their limits.
Ideal for:
- Jigs, fixtures, and tooling
- Turbines and fan blades
- Fluid and airflow components
- Electrical casings and automotive housings
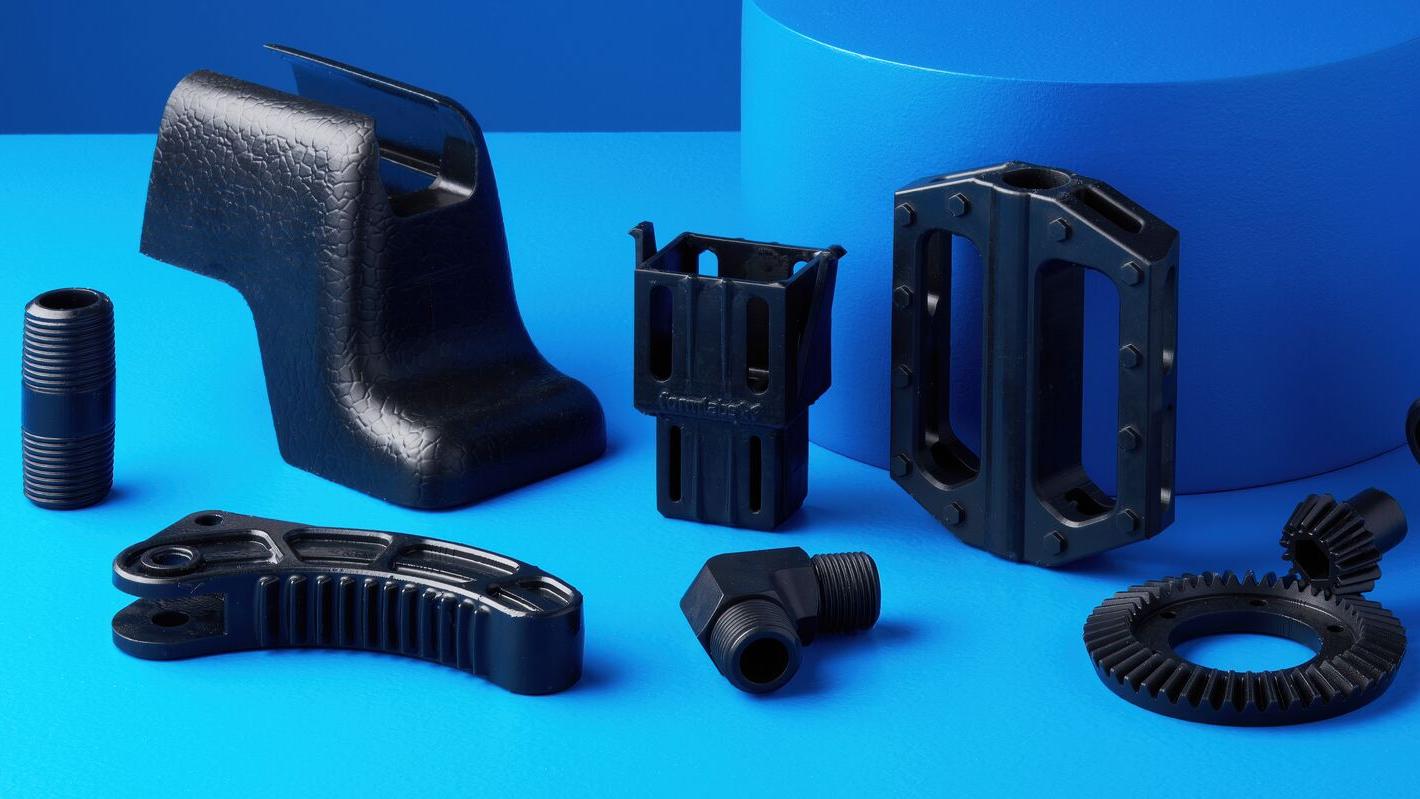

Specialty Resins
Push the limits of 3D printing
Our Specialty Resins features advanced materials with unique mechanical properties that expand what’s possible with in-house fabrication on our stereolithography 3D printers. Resin options include:
- High Temp Resin: Detailed, Precise Prototypes With High Temperature Resistance
- Flame Retardant (FR) Resin: UL 94 V-0 Certified 3D Printed Parts With Excellent Quality and Heat Resistance
- ESD Resin: A rugged ESD-safe material to improve your electronics manufacturing workflows.

Medical Resins
3D Printing Materials for Healthcare.
Our BioMed Resins are designed for healthcare professionals who are seeking medical-grade materials for a wide range of applications where performance and biocompatibility are critical. Materials in our BioMed Resin family are developed and manufactured in an ISO 13485 certified facility and are compatible with common disinfection and sterilization methods.
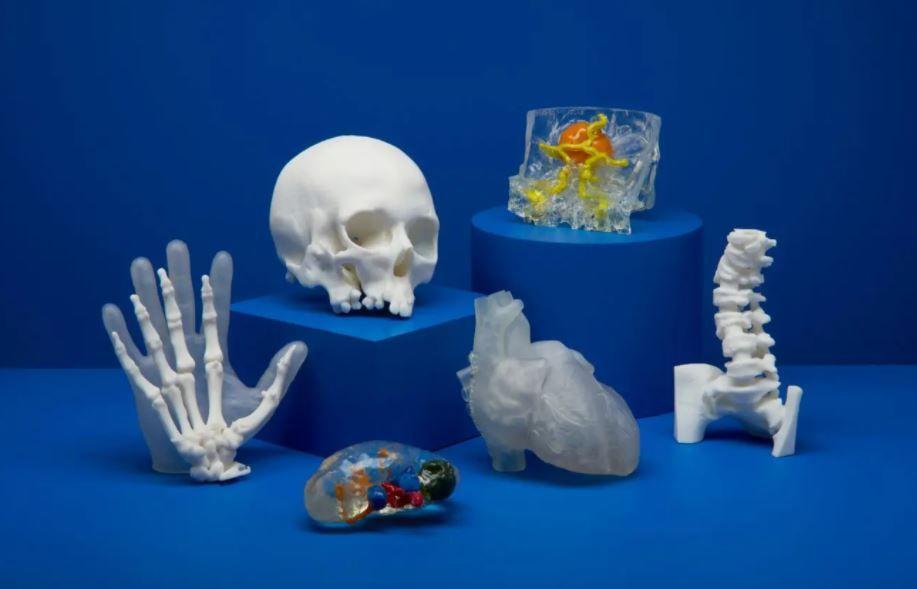
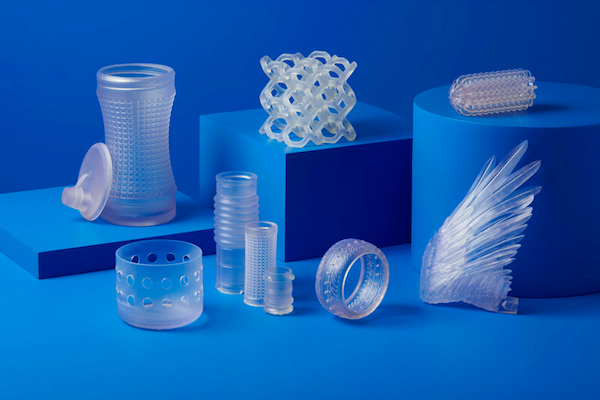
Flexible and Elastic Resins
Functional prototyping materials
Replace outsourcing and molding of silicone, urethane, and rubber parts. With Formlabs 3D printers, it’s possible to produce flexible parts in-house in a matter of hours using our family of Flexible and Elastic Resins.
Ideal for:
- Consumer goods prototyping
- Compliant features for robotics
- Medical devices and anatomical models
- Special effects props and models

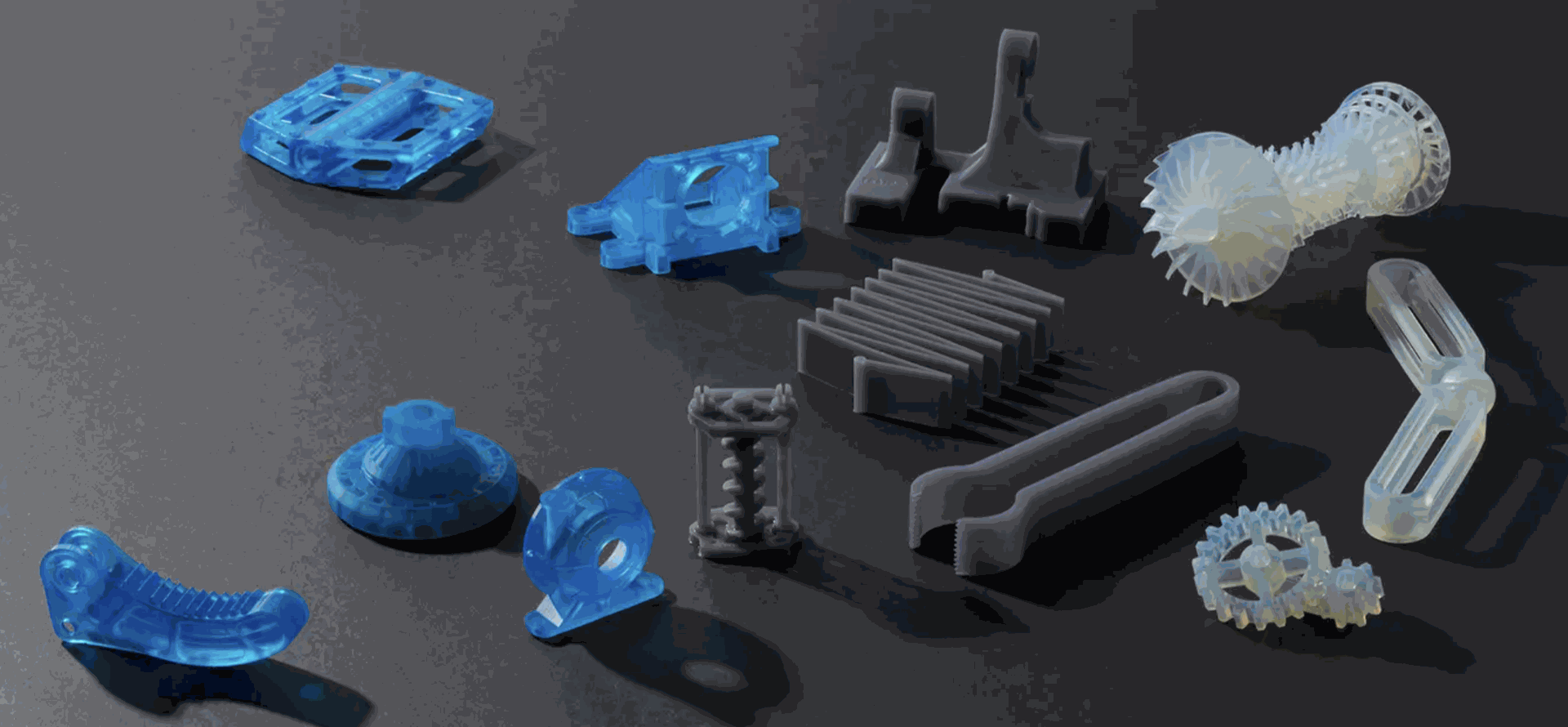
Tough and Durable
Outstanding performance. Excellent detail.
Our most robust, functional, and dynamic materials, our family of Tough and Durable Resins can handle compression, stretching, bending, and impacts without breaking. Choose these resins when bending at lower stress levels is preferred to a brittle failure.
Ideal for:
- Housings and enclosures
- Jigs and fixtures
- Connectors
- Wear-and-tear prototypes
Top 10 Advantages of 3D Printing
Speed
One of the biggest advantages of 3D printing technology is Rapid Prototyping. Rapid prototyping is the ability to design, manufacture, and test a customized part in as little time as possible. Also, if needed, the design can be modified without adversely affecting the speed of the manufacturing process. Before 3D printing industry came to flourish, a prototype would take weeks to manufacture. Every time a change was made, another few weeks of time were added to the process. With shipping times figured in, fully developing a product from start to finish could easily take a year. With 3D printing, this can be done in as little as 2-3 days. For small production runs and prototyping, 3D printing is the best option as far as speed is concerned.
Flexibility
Another big advantage of 3D printing is that any given printer can create almost anything that fits within its build volume. With traditional manufacturing processes, each new part or change in part design, requires a new tool, mold, die, or jig to be manufactured to create the new part. In 3D printing, the design is fed into slicer software, needed supports added, and
then printed with little or no change at all in the physical machinery or equipment. 3D printing allows the creation and manufacture of geometries impossible for traditional methods to produce, either as a single part, or at all. Such geometries include hollow cavities within solid parts and parts within parts.
Cost
For small production runs and applications, 3D printing is the most cost-effective manufacturing process. Traditional prototyping methods like CNC machining and injection molding require a large number of expensive machines plus they have much higher labor costs as they require experienced machine operators and technicians to run them. This contrasts with 3D printing process, where only 1 or 2 machines and fewer operators are needed to manufacture a part. There is far less waste material because the part is built from the ground up, not carved out of a solid block as it is in subtractive manufacturing and usually does not require additional tooling.
Competitive Advantage
Because of the speed and lower costs of 3D printing, product life cycles are reduced. Businesses can improve and enhance a product allowing them to deliver better products in a shorter amount of time. 3D printing allows the physical demonstration of a new product to customers and investors instead of leaving it to their imaginations, therefore reducing the risk of information being misunderstood or lost during communication. It also allows for cost-effective market testing, obtaining feedback from potential customers and investors on a tangible product, without the risk of large upfront expenditures for prototyping.
Quality Control
Traditional manufacturing methods can result in poor designs therefore poor quality prototypes. Imagine baking a cake, where all the ingredients are combined and mixed together, then placed in the oven to bake. If it happens the elements were not mixed well, the cake would have problems like air bubbles or fail to bake thoroughly. The same can occur with subtractive or injection methods; quality is not always assured. The nature of 3D printing allows the step-by-step assembly of the part or product, which guarantees enhancement of the design and better quality parts/products.
Tangible Design & Product Testing
Seeing a product on a screen cannot compare with actually touching and feeling a prototype. A physical prototype can be tested and if flaws are found, the CAD file can be modified and a new version printed out by the next day. This rapid prototyping not only speeds up the development process but also allows for immediate and precise adjustments, ensuring a more accurate and high-quality final product. Additionally, this hands-on approach significantly enhances the team's understanding of the product's practical applications and user experience, leading to more innovative and user-centric designs.
Sustainability
With 3D printing, fewer parts need outsourcing for manufacturing. This equals less environmental impact because fewer things are being shipped across the globe and there is no need to operate and maintain an energy-consuming factory. Additionally, this localized production method significantly reduces the carbon footprint associated with transportation and logistics, further contributing to a more sustainable manufacturing process. Moreover, it allows for more responsive and adaptable manufacturing, enabling businesses to quickly adjust to market demands or design changes without excessive inventory or waste.
Consistency
Traditional manufacturing processes can result in a percentage of a batch of parts being defective or inconsistent in quality compared to the rest of the parts. In 3D printing, the parts are printed in succession. Each successive individual part can be monitored, allowing errors to be caught in real time, reducing the overall number of failed parts and wasted materials while increasing the consistent quality of the parts produced. Furthermore, this process enables immediate adjustments to be made for subsequent prints, enhancing the precision and reliability of each component. This level of quality control is particularly beneficial in industries where high standards and specifications are crucial, leading to more dependable and efficient production outcomes.
Risk Reduction
3D printing technology enables product designers to verify product prototypes before embarking on substantial manufacturing investments that can be potentially disastrous. This capability to test and refine designs with minimal upfront cost not only safeguards against the financial risks associated with large-scale production errors but also ensures that the final product meets the desired standards and specifications. Moreover, it facilitates a more agile development process, where design modifications can be implemented swiftly, allowing for the rapid evolution of products in response to market feedback or technological advancements. This adaptability is crucial in today's fast-paced market, where the ability to quickly respond to changing consumer needs and industry trends can provide a significant competitive advantage.
Accessibility
3D printing systems are much more accessible and can be used by a wider range of people compared to traditional manufacturing setups. The cost of setting up a 3D printing operation is significantly lower than traditional systems, making it a financially viable option for many. Additionally, 3D printing is largely automated, reducing the need for extensive personnel to operate, supervise, and maintain the machines. This accessibility greatly benefits small businesses and individual entrepreneurs, allowing them to engage in product innovation and production without hefty capital investments. The technology's flexibility in customization and rapid prototyping also makes it ideal for industries requiring tailored solutions or fast product development, thereby democratizing the manufacturing process and encouraging creative and entrepreneurial ventures across various fields.